Laser Skin Treatments Overview in the United States
Laser skin treatments in the United States involve various technologies to address skin texture, pigmentation, scars, and signs of aging. These procedures have evolved to offer options suitable for different skin types with varied recovery times, costs, and treatment goals relevant for 2026.
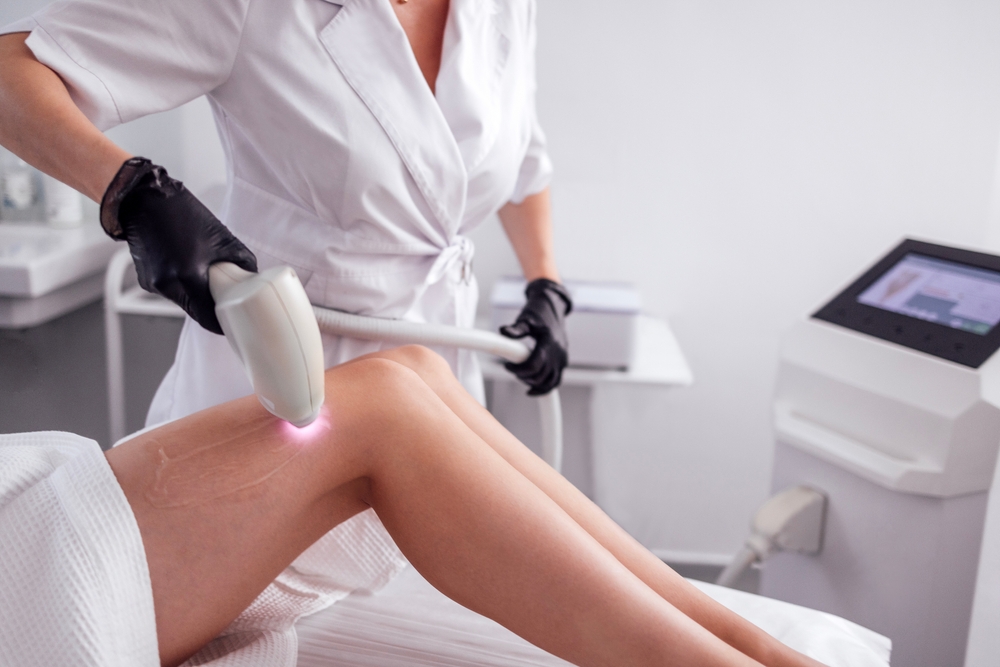

How Laser Skin Treatments Work
Laser skin treatments utilize concentrated light energy targeted at specific layers of the skin. The purpose is to induce controlled damage that stimulates the body’s natural healing processes, such as collagen and elastin production, which can improve skin texture, firmness, and overall appearance. Different laser systems vary in wavelength, pulse duration, and energy, affecting the depth and type of skin interaction.
Common types of lasers used in 2026 include ablative and non-ablative lasers. Ablative lasers remove the outer skin layers and are usually employed for deeper resurfacing needs, such as significant wrinkles or acne scars. Non-ablative lasers work by heating the underlying skin tissue without removing the surface, promoting collagen growth with generally shorter recovery periods.
Common Laser Technologies in Use (2026)
- Fractional CO₂ Laser: Delivers fractional columns of laser light, targeting small skin areas while leaving surrounding tissue intact, which enhances healing.
- Erbium YAG Laser: Primarily used for precise ablation with less thermal damage compared to CO₂ lasers.
- Picosecond Lasers: Employ ultra-short pulses to target pigmentation and stimulate collagen with minimal downtime.
- Nd:YAG Laser: Typically used for deeper skin layers, including for vascular conditions and hair removal.
- Diode Lasers: Often used in hair removal but also applicable in some skin rejuvenation procedures.
Treatment Areas and Applications
Laser treatments are mainly applied to the face, but also commonly used on the neck, chest, and hands. Treatment goals may include:
- Reduction of fine lines and wrinkles
- Improvement of acne and surgical scars
- Correction of uneven skin tone and pigmentation
- Skin tightening and texture enhancement
The choice of laser and treatment protocol depends on the specific skin concern and patient skin type.
Treatment Sessions and Procedure Overview
Typical laser skin treatment involves multiple sessions, often spaced several weeks apart, to achieve gradual improvement. A series usually includes 3 to 5 treatments, although some patients may experience noticeable changes earlier depending on laser type and skin condition.
Sessions can range from 20 minutes to an hour depending on the size of the treatment area and technology. Numbing creams or local anesthetic may be applied to manage discomfort during the procedure.
Post-treatment effects commonly include redness, swelling, peeling, and sensitivity similar to mild sunburn. Recovery duration varies widely by laser type — non-ablative lasers may allow return to normal activities the same day or within a few days, while ablative procedures can require one to two weeks or longer for healing.
Patients are generally advised to avoid direct sun exposure and use appropriate skin care after treatments to support healing and reduce risks.
Suitability and Skin Type Considerations
Laser treatments can be adapted for various Fitzpatrick skin types (I-VI), although some lasers may carry risks of pigmentation changes in darker skin tones. Advances in laser technology have increased options available for deeper skin tones, with careful adjustment of settings and protocols essential to reduce adverse effects.
Consultation with medical professionals who assess skin type, medical history, and treatment goals is important in determining the safest and most effective approach.
Safety and Side Effects
Laser skin treatments carry potential side effects, including:
- Temporary redness and swelling
- Peeling and flaking
- Hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation
- Infection (rare with proper care)
- Scarring (rare with experienced providers and appropriate technique)
Adherence to pre- and post-treatment guidelines, including sun protection and skin care, is critical to minimizing complications.
Typical Costs in United States (2026)
When considering laser skin treatments in the United States, typical price ranges include:
- Basic option: Around $300 to $600 per session – generally non-ablative lasers for mild skin texture improvements and pigmentation issues.
- Standard option: Approximately $700 to $1,500 per session – often fractional resurfacing lasers targeting moderate wrinkles, scars, and pigmentation.
- Premium option: Typically $1,500 to $3,000 or more per session – includes advanced ablative lasers or combined treatment protocols for extensive skin rejuvenation.
Prices can vary depending on geographic location, the expertise of the provider, the area treated, and the number of sessions planned.
Technological Developments in 2026
Emerging technologies in laser skin treatments continue to refine precision, safety, and patient comfort. Developments include:
- Laser-Coring™ and UltraClear™ Systems: Designed to target deeper tissue layers efficiently with reduced downtime.
- 3DMIRACL™ Laser Resurfacing: Offers three-dimensional targeting of skin irregularities for customized treatment.
- Next-generation Picosecond Lasers: Enhanced ability to treat pigmentation and stimulate collagen with lower risk for all skin types.
These innovations reflect ongoing efforts to broaden safe treatment options for diverse skin tones, minimize recovery time, and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Laser skin treatments in the United States remain a widely used method for addressing various dermatological concerns in 2026. Understanding the types of lasers, treatment processes, potential side effects, and general cost considerations can assist individuals in making informed decisions. Skin type and condition assessments by qualified professionals are essential steps prior to starting any laser treatment regimen.