Innovative modular housing concept to create efficient living spaces
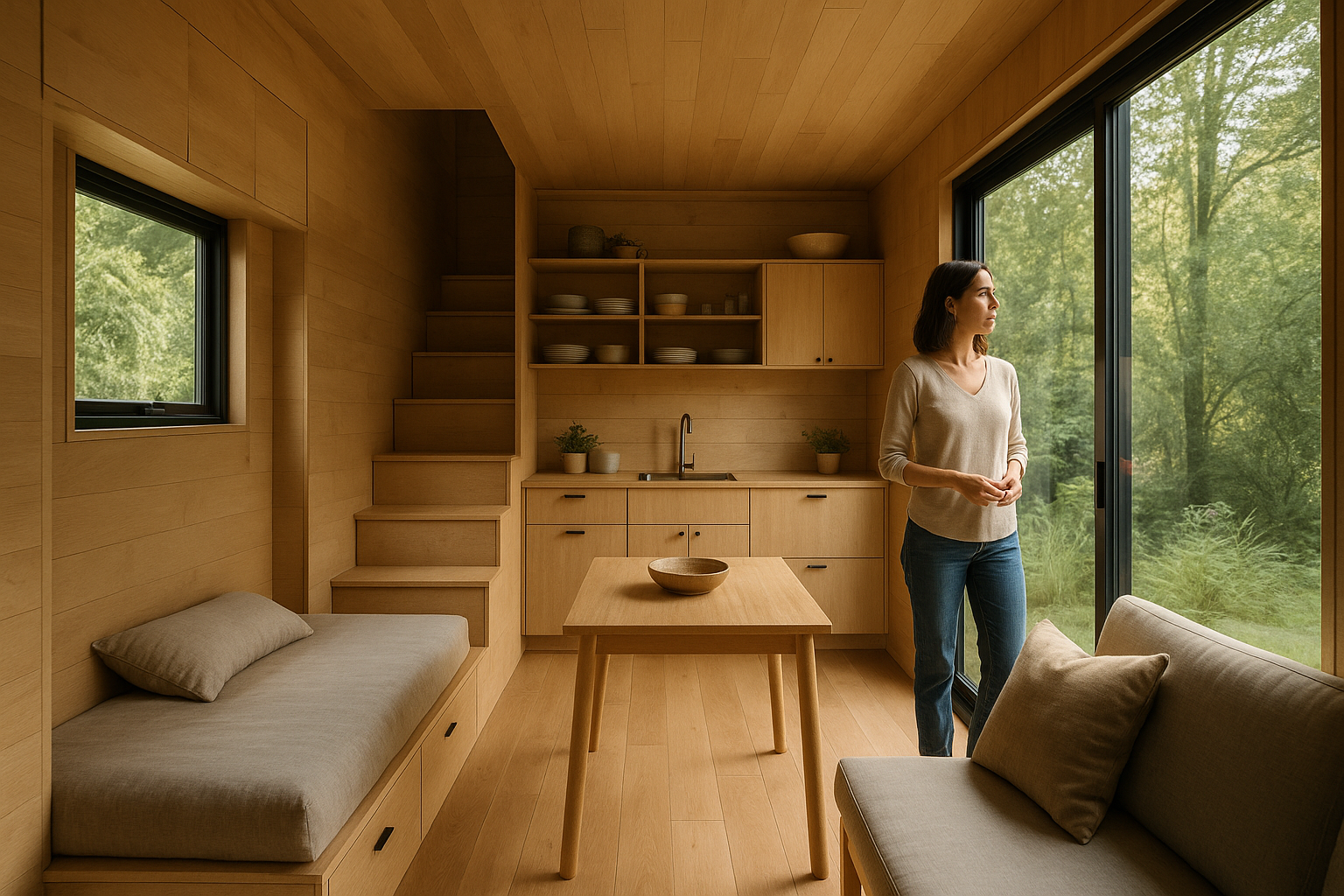
Modular housing represents a transformative approach to residential construction that challenges traditional building methods. By assembling prefabricated sections in controlled factory environments before transporting them to final locations, this housing concept offers streamlined construction timelines, reduced waste, and flexible design possibilities. As housing affordability and sustainability become pressing concerns across the United States, modular homes present an increasingly viable solution for families, developers, and communities seeking efficient, quality living spaces without the lengthy construction periods associated with conventional builds.

What Is Modular Housing?
Modular housing refers to homes constructed in sections or modules within a controlled factory environment before being transported and assembled at the final building site. Unlike traditional stick-built homes constructed entirely on-site, modular homes are built in climate-controlled facilities where quality control measures can be consistently applied. Each module typically includes finished walls, flooring, ceilings, electrical systems, and plumbing. Once transported to the property, these sections are joined together on a permanent foundation, creating a complete residential structure. Modular construction should not be confused with mobile homes or manufactured housing, as modular homes must meet the same local building codes and standards as site-built homes. The construction process allows for simultaneous site preparation and module fabrication, significantly reducing overall project timelines.
Space Efficiency in Modular Homes
Modular homes excel at maximizing usable living space through thoughtful design and precise manufacturing processes. Factory construction eliminates many of the dimensional variations that occur in traditional building, resulting in tighter seams and more accurate measurements. This precision allows designers to optimize every square foot without sacrificing structural integrity. Open floor plans are easily achieved in modular construction, creating flowing spaces that feel larger than their actual footprint. Multi-functional rooms and built-in storage solutions are commonly integrated into modular designs, reducing wasted space. The standardized nature of module dimensions encourages efficient layouts that minimize hallways and transitional areas. Vertical space utilization through higher ceilings and loft areas further enhances the sense of openness. Many modular manufacturers offer customizable floor plans that can be adapted to specific lot sizes and family needs while maintaining spatial efficiency.
Sustainable Living with Modular Homes
Modular construction inherently supports sustainable building practices through reduced material waste and controlled manufacturing environments. Factory settings allow for precise material ordering and cutting, with excess materials often recycled into subsequent projects rather than ending up in landfills. The controlled environment protects building materials from weather-related damage and degradation that commonly occurs during traditional construction. Many modular home manufacturers incorporate energy-efficient features such as enhanced insulation, high-performance windows, and efficient HVAC systems as standard offerings. The shorter construction timeline reduces the environmental impact of construction sites, including soil disruption and local air quality effects. Transportation of modules does require fuel consumption, but this is often offset by the reduced number of material delivery trips required compared to traditional construction. Some manufacturers specifically focus on sustainable materials, including recycled content, renewable resources, and low-VOC finishes. The tight construction tolerances achieved in factory settings result in homes with better air sealing, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling throughout the home’s lifetime.
Cost Considerations for Modular Homes
Understanding the financial aspects of modular home construction requires examining both base costs and additional expenses. The factory-built modules themselves typically range from $50 to $100 per square foot for basic models, with custom designs and premium finishes increasing costs to $100 to $200 per square foot. These figures represent the modules only and do not include land, site preparation, foundation work, utility connections, or final assembly. Total project costs including all components generally range from $100,000 for small basic homes to $300,000 or more for larger custom designs. Site preparation costs vary significantly based on location and existing conditions but typically add $10,000 to $30,000. Foundation work adds another $15,000 to $40,000 depending on design requirements. Transportation and crane services for module placement generally cost between $5,000 and $15,000. Final assembly, finishing work, and utility connections can add $20,000 to $50,000 to the total project budget.
| Cost Component | Typical Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Base Module Cost | $50-$200 per sq ft | Varies by customization level |
| Site Preparation | $10,000-$30,000 | Depends on terrain and access |
| Foundation | $15,000-$40,000 | Based on design requirements |
| Transportation & Crane | $5,000-$15,000 | Distance and module count |
| Assembly & Finishing | $20,000-$50,000 | Includes utilities connection |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
From Design to Move-In: The Modular Home Process
The modular home journey begins with design selection or customization, where buyers work with manufacturers to choose floor plans, finishes, and features. This phase typically takes two to four weeks as designs are finalized and engineering plans are completed. Simultaneously, site preparation begins, including land clearing, utility planning, and foundation construction. Once designs are approved, factory construction commences, usually requiring six to twelve weeks depending on home size and complexity. During this period, quality inspections occur at multiple stages to ensure compliance with building codes. When modules are complete, they are wrapped for protection and transported to the building site, a process that may take one to three days depending on distance. On-site assembly typically occurs within one to two weeks, as modules are positioned, joined, and sealed. Final finishing work, including connecting utilities, completing interior details, and exterior touches, requires an additional two to four weeks. From initial design to move-in, the entire process generally spans three to six months, roughly half the time required for comparable traditional construction. Local building inspectors conduct final reviews before occupancy permits are issued, ensuring all work meets applicable codes and standards.
Understanding Long-Term Value
Modular homes built to local building codes appreciate in value similarly to site-built homes, dispelling common misconceptions about their long-term worth. Financing options for code-compliant modular homes mirror those available for traditional construction, with conventional mortgages, FHA loans, and VA loans all applicable. Insurance providers treat properly constructed modular homes identically to site-built homes, with premiums based on location, coverage, and home value rather than construction method. Maintenance requirements for modular homes align with traditional homes, focusing on regular upkeep of roofing, mechanical systems, and exterior finishes. The quality of factory construction often results in fewer warranty claims and structural issues during the first years of ownership. Resale potential depends primarily on location, design quality, and market conditions rather than the modular construction method. Energy efficiency features common in modular homes can provide ongoing cost savings that enhance overall value. As modular construction becomes more widely understood and accepted, market perceptions continue to shift positively, supporting strong resale values for well-maintained homes.