Innovative Modular and Container Homes Promoting Sustainable, Energy-Efficient Living in the United States in 2025
Explore how modular and container homes are contributing to sustainable and energy-efficient housing solutions in the United States by reducing construction waste, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting innovative design techniques that optimize energy use and resource conservation.
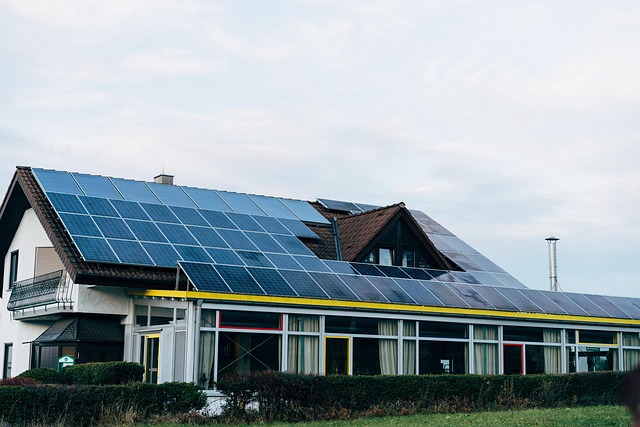

In 2025, innovative modular and container homes stand at the forefront of sustainable, energy-efficient living across the United States. These homes leverage repurposed shipping containers combined with modern architectural design and green technologies to deliver eco-friendly, affordable, and rapidly constructed residences. By reusing durable steel containers and integrating advanced insulation, renewable energy systems, and smart home features, container homes offer a compelling alternative to conventional building, reducing construction waste by up to 50% and lowering costs by 20-30%.
What Are Modular Container Homes?
Modular container homes are residential spaces created by converting shipping containers—typically 20 or 40 feet long—into livable units. These boxes of steel are engineered to be structurally robust, designed originally to withstand ocean voyages and heavy stacking, making them resilient against various weather conditions when properly modified and anchored.
Modularity means these containers can be stacked vertically or arranged horizontally to customize the size and layout of the home. This approach supports creative architectural configurations—from compact single units to multi-story, courtyard, or L-shaped homes, with flexible phases of expansion as family needs evolve.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Container homes embody sustainability on multiple levels:
- Recycling Steel: Each container repurposed diverts approximately 3,500 kg of steel from scrap yards, minimizing resource extraction.
- Reduced Construction Waste: Container-based construction cuts building waste by roughly 50% compared to traditional methods.
- Efficient Land Use: Stacked or dense modular designs maximize space, often requiring smaller footprints, helpful for urban or limited land settings.
- Green Roofs and Rooftop Gardens: Many designs integrate vegetated roofs that provide insulation, manage rainwater, enhance biodiversity, and mitigate urban heat island effects.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Containers’ flat roofs facilitate rainwater collection systems to supply irrigation and household water demands after filtration.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar panels can be installed on flat container roofs, often allowing homes to incorporate renewable energy sources.
By reducing demand for new raw materials and embracing clean energy solutions, container homes support environmentally responsible housing initiatives in the United States.
Energy Efficiency Features
One challenge of steel container homes is steel’s high thermal conductivity, which requires expert insulation to maintain comfort and reduce energy demand:
- Advanced Insulation Techniques: Spray foam insulation, rigid foam boards with air gaps, and exterior cladding systems are common methods to prevent heat loss and condensation issues.
- Ventilation: Strategically positioned operable windows, energy-recovery ventilators, ceiling fans, and mechanical ventilation systems optimize airflow and indoor air quality.
- Natural Lighting: Large windows, sliding glass doors, and skylights flood interiors with daylight, minimizing electricity usage.
- Mini-Split Heat Pumps: These compact, efficient HVAC units are ideal for container homes that lack ductwork, providing heating and cooling with reduced energy consumption.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: ENERGY STAR-rated compact appliances fit container living spaces while lowering power use.
Together, these measures help container homes adapt to diverse U.S. climates with improved energy efficiency.
Cost and Construction Timelines
Container homes offer potential cost and time advantages:
- Cost Savings: Container homes typically cost less than comparable traditional homes. Entry-level single-container homes may start around $25,000-$35,000, while custom multi-container homes with sustainable features can range between $120,000 and $180,000 for 1,000 to 1,500 square feet.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Faster modular assembly and shorter construction times (2-4 months versus 6-12 months for traditional houses) can reduce labor expenses.
- Additional Expenses: Modifications like cutting openings for windows and doors, adding insulation, foundation work, and hooking up utilities require professional engineering and add to costs.
- Land Costs: Land purchase remains a separate cost that varies by location.
The combination of recycled base structures, streamlined building processes, and sustainability incentives contributes to the affordability of container homes.
Design Flexibility and Lifestyle Benefits
The modular nature offers versatility and personalization:
- Expandable Layouts: Start with one container and add more units as needs evolve.
- Multi-Functional Interiors: Built-in furniture, Murphy beds, convertible rooms, under-floor storage, and multi-use staircases maximize compact space.
- Accessibility Options: Single-story designs, wider doorways, and zero-threshold entrances support mobility needs.
- Outdoor Living: Roof terraces, covered porches, and courtyard arrangements enhance quality of life.
- Personalization: Aesthetic finishes, from exposed metal to wood paneling or drywall, combined with smart technologies tailor homes to occupant preferences.
This flexibility helps accommodate various lifestyles, including singles, families, and remote workers seeking efficient living spaces.
Navigating Regulations and Permits
Regulations for container homes vary across the United States:
- Building Codes: Homes must meet structural, fire safety, energy efficiency, electrical, plumbing, and mechanical standards comparable to conventional dwellings.
- Permits: Detailed architectural and engineering plans are usually required for permit approval.
- Zoning: Some jurisdictions impose minimum square footage, aesthetic guidelines, or restrict container homes in certain zones.
- Specialized Expertise: Working with architects and companies familiar with container home regulations helps navigate these requirements effectively.
Understanding and complying with local rules is essential for legal and safe construction.
The Container Home Market Outlook in the United States
Market growth for container homes in the U.S. continues in 2025, supported by:
- Demand for Affordable Housing: Rising housing costs increase interest in modular container homes.
- Technological Innovation: AI-driven design customization, robotics in manufacturing, and AR/VR visualization tools support design precision and efficiency.
- Sustainability Focus: Environmental concerns encourage the adoption of green building practices.
- Growth Projections: The global container home market is valued at about $70.49 billion in 2025 and expected to rise steadily, with North America as a significant market.
Different regions have varying levels of adoption and incentives, but container homes remain a growing segment in residential construction.
Longevity and Maintenance
Container homes provide durable and relatively low-maintenance housing options:
- Steel Construction: Resistant to rot, termites, and pests compared to traditional wood framing.
- Corrosion Protection: Marine-grade coatings prevent rust; regular repainting and moisture control maintain structural integrity.
- Life Expectancy: With routine maintenance, container homes can last 25-50 years or more.
- Energy Savings and Durability: Effective insulation and sustainable materials help reduce long-term repair and utility costs.
This durability supports container homes as a sustainable housing solution.
Conclusion
Modular and container homes offer an informative example of innovative approaches to sustainable and energy-efficient residential living in the United States. By repurposing steel containers, integrating advanced insulation and ventilation, incorporating renewable energy options, and enabling flexible designs, these homes provide insights into emerging eco-conscious housing trends. As technology advances and market interest grows, container homes continue to be an area worth understanding for their potential contributions to affordable and sustainable living environments.
Sources
- Hutter Architects - Eco Cargo Container House Plans
- Conexwest - Best US States for Shipping Container Homes in 2025
- Precedence Research - Container Homes Market Disclaimer: All content, including text, graphics, images and information, contained on or available through this web site is for general information purposes only. The information and materials contained in these pages and the terms, conditions and descriptions that appear, are subject to change without notice.