General Maintenance Considerations for Residential Swimming Pools
Dive into 2026 with peace of mind by mastering essential swimming pool maintenance for your US home. From prepping for summer BBQs to tackling seasonal weather shifts, discover how to keep your backyard pool sparkling, safe, and ready for endless family fun.
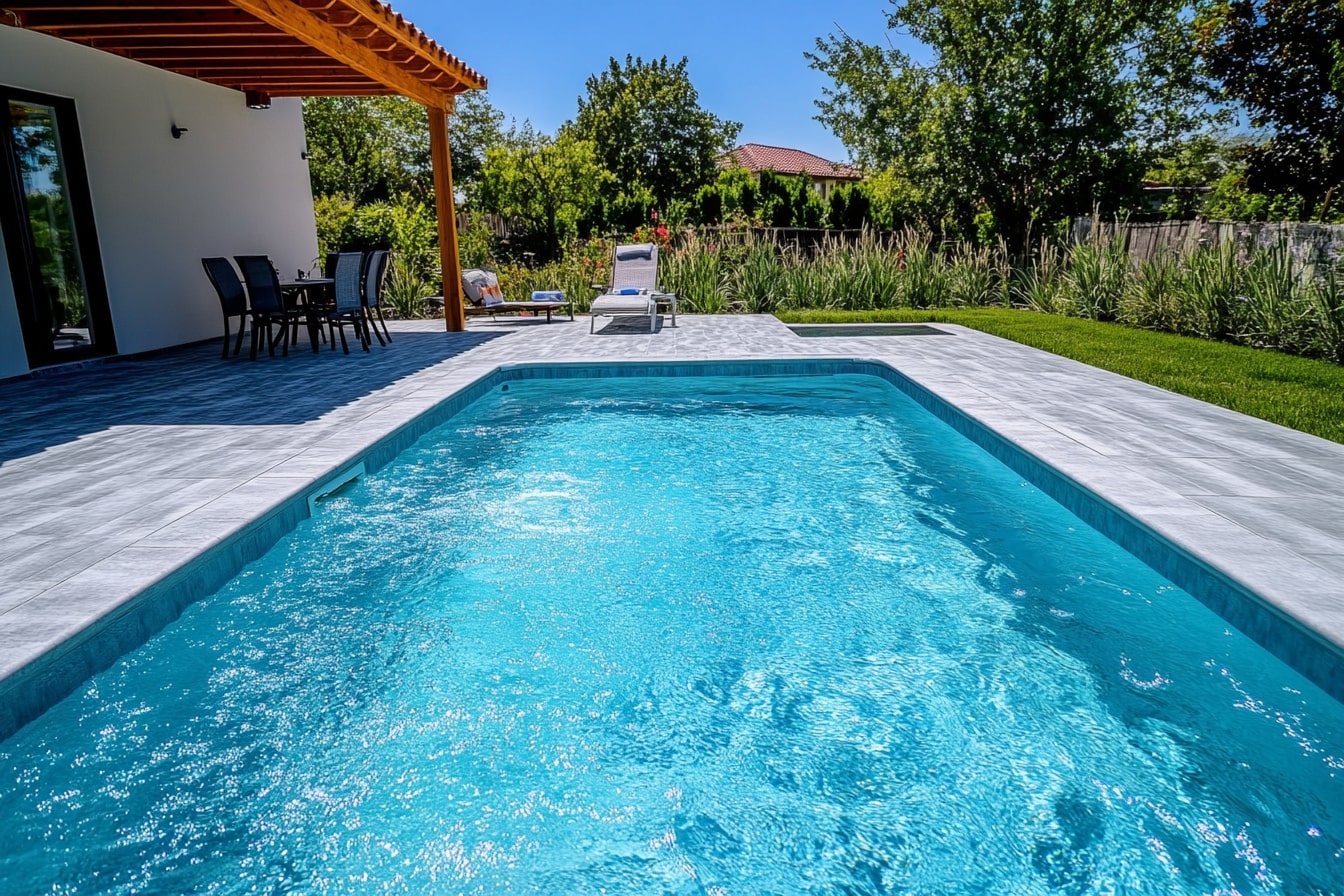

Residential swimming pools add comfort and value to a property, but they only stay inviting when the water is clear, the systems are functioning well, and safety is always in mind. A regular maintenance routine reduces algae growth, equipment failures, and safety risks so that the pool remains ready to use throughout the swimming season.
Seasonal pool care tips for US homeowners
Pool care needs shift with the seasons in the United States, especially in regions with cold winters and hot summers. At the start of spring, it is important to remove debris, inspect the pool structure, and check for cracks, loose tiles, or damaged coping. Homeowners should also clean or replace filters, test water chemistry, and confirm that pumps and heaters start up normally.
During peak summer months, higher temperatures and heavier pool use can quickly throw off water balance. Brushing walls and steps, vacuuming the floor, and skimming the surface several times a week helps limit algae and organic buildup. Keeping a consistent schedule for testing and adjusting chemicals, usually at least two or three times a week in heavy use, prevents cloudy water and irritation to skin and eyes.
As temperatures drop in fall, it is smart to remove leaves and begin gradually reducing pump run times while still maintaining safe water balance. In colder parts of the country, winterizing is essential. That typically involves lowering the water level if required, blowing out lines, adding winter chemicals, and securely covering the pool to protect it from debris and ice damage.
Water quality management and testing
Water quality management is at the heart of residential pool maintenance. Proper chemistry keeps water clear, comfortable, and less likely to harbor harmful microorganisms. Key parameters usually include free chlorine or another sanitizer level, pH, total alkalinity, calcium hardness, and stabilizer. Each of these factors affects how well sanitizers work and how the water interacts with pool surfaces and equipment.
Homeowners can use test strips or liquid test kits to measure these levels. For best results, testing at least weekly during light use and more often during peak season is advised. If readings fall outside recommended ranges, adjustments should be made gradually using appropriate products. For example, if pH drifts too high, it can reduce sanitizer effectiveness and cause scaling; if too low, it can lead to corrosion and discomfort for swimmers.
Occasional professional water testing at a local pool store adds another layer of assurance. These services often provide more detailed readings and can detect issues like high dissolved solids or metal content that might not appear on basic home tests. Keeping a simple log of test results and adjustments helps identify recurring patterns and refine the maintenance routine.
Equipment maintenance and troubleshooting
Circulation and filtration systems keep water moving and remove fine particles that cloud the pool. Pumps, filters, heaters, chlorinators, and robotic cleaners all work together, and each needs periodic attention. Routine tasks include emptying skimmer and pump baskets, rinsing or backwashing filters according to the manufacturer instructions, and checking for leaks or unusual noises.
If the pump loses prime or makes grinding sounds, that can point to air leaks, clogged baskets, or worn bearings. Reduced water flow may suggest a dirty filter, blocked skimmer, or valves that are not fully open. Addressing small issues quickly prevents them from turning into larger and more costly repairs. When in doubt, consulting the equipment manual or contacting a qualified pool technician is often the safest option.
Electrical components and automation systems should also be inspected regularly. Loose connections, corroded terminals, or malfunctioning timers can affect both safety and efficiency. Ensuring that all equipment is properly grounded and that any repairs follow local electrical codes helps reduce the risk of shocks and failures.
Safety measures and compliance standards
Safety considerations are just as important as water clarity and comfort. Barriers, alarms, and clear rules around pool use help reduce the risk of accidents, especially for households with children or pets. Many areas in the United States require specific types of fencing, self latching gates, or door alarms for residential pools, so homeowners should review local building codes and regulations.
Non slip surfaces around the deck, handrails on steps, and clearly visible depth markers contribute to a safer environment. Regularly inspecting for loose tiles, cracked concrete, or damaged ladders can prevent slips and falls. Proper storage of pool chemicals in a cool, dry, and locked area keeps them away from children and reduces the chance of spills or dangerous reactions.
Emergency preparedness is another key part of pool safety. Keeping rescue equipment such as a life ring and reaching pole close to the pool, along with a well stocked first aid kit, can make a difference in an urgent situation. Posting simple rules, such as no running on the deck and no diving in shallow water, reinforces safe behavior for guests.
Sustainable practices and energy efficiency
Energy and water conservation are growing priorities for many homeowners. Simple changes in how a pool is operated can reduce utility use and environmental impact. For example, running the pump during off peak electricity hours when possible, and only for as long as needed to properly circulate the water, can cut energy consumption. Variable speed pumps, though an investment, often provide significant efficiency gains compared to older single speed models.
Solar covers help limit heat loss and reduce evaporation, which lowers both heating costs and water use. In warmer climates, some homeowners also use solar heating panels to extend the swimming season with less reliance on gas or electric heaters. Choosing energy efficient LED lighting for underwater and landscape fixtures around the pool further decreases electricity demand.
Water saving measures include promptly fixing leaks, using a cover during windy periods, and avoiding unnecessary draining. When partial draining is required to correct water chemistry, directing the water to appropriate drainage areas and following local discharge rules helps protect surrounding soil and stormwater systems.
A thoughtful maintenance plan that balances comfort, safety, and resource use allows residential pools to remain enjoyable for years. By paying attention to seasonal needs, monitoring water quality, caring for equipment, following safety guidelines, and adopting efficient practices, homeowners can keep their pools in good condition while managing costs and environmental impact.