Exploring the Benefits and Considerations of Steel Roofing
Steel roofing has emerged as a popular choice for homeowners seeking durability and long-term value. This roofing material offers exceptional resistance to weather elements while providing energy efficiency benefits that can reduce utility costs over time. Understanding the various aspects of steel roofing, from installation requirements to maintenance considerations, helps property owners make informed decisions about this significant investment in their home's protection and value.
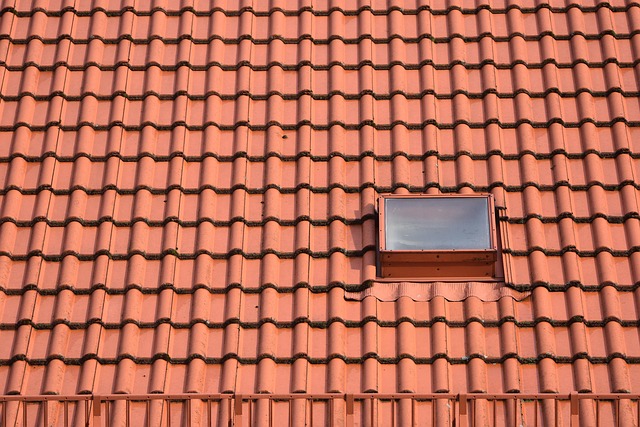

Steel roofing plays an increasingly important role in residential and commercial construction in the United States. Advances in coatings, colors, and profiles have helped move this material from industrial settings to everyday neighborhoods. Understanding how steel roofing works, where it performs best, and what to consider before installation can help align expectations with real world performance.
Introduction to steel roofing
Steel roofing is a type of metal roofing system made primarily from coated steel panels or shingles. It is typically formed from thin sheets of steel that are galvanized or coated with other protective finishes to resist corrosion. These panels can be installed on houses, garages, barns, and commercial buildings, often over a solid deck with an underlayment layer.
In the United States, steel roofing is valued for its combination of strength and relatively low weight compared with materials such as concrete tiles. Many systems are engineered to meet building code requirements for wind uplift and fire resistance, which can be important in regions affected by severe storms or wildfire risk. Because it is manufactured in standardized profiles and lengths, steel roofing can offer consistent quality when properly installed.
Advantages of steel roofing
One frequently cited advantage of steel roofing is its long service life when maintained and installed correctly. Unlike some traditional materials that may need replacement after a couple of decades, steel systems are often designed to remain functional for several decades, depending on climate, maintenance, and product quality. Protective coatings help resist rust, fading, and surface wear.
Steel roofing can also contribute to energy performance. Many products include reflective paint systems that help reduce heat absorption from the sun. In warm or sunny climates, this can support a more stable indoor temperature when combined with appropriate insulation and ventilation. The reduced weight of steel roofing compared with certain alternatives can also lessen structural load on the building.
Another advantage is fire resistance. Noncombustible metal panels do not ignite in the way that wood shakes or some older roofing materials can, which may be beneficial in areas prone to wildfires or where building codes emphasize fire performance. Additionally, steel roofing can be compatible with rainwater collection systems because the surface tends to shed water efficiently, especially when roof slopes and gutters are designed correctly.
Types of steel roofing
Steel roofing is available in several profiles and formats, each with its own appearance and performance characteristics. One common option is standing seam, which features long vertical panels with raised seams where the panels connect. This style is often chosen for its clean lines and strong weather resistance, since many standing seam systems rely on concealed fasteners and interlocking seams.
Another category includes metal shingles or tiles made from steel. These products are manufactured to resemble traditional shingles, slate, or even tile, while offering the benefits of metal. They can suit projects where a more conventional residential look is desired but the owner prefers the characteristics of steel.
Corrugated or ribbed steel panels are frequently used on agricultural or light commercial buildings. These panels have repeating ridges that add strength and help water run off the surface. While they can be used on houses, they are more common on barns, sheds, and workshops, where a utilitarian appearance is acceptable or preferred.
Resilience and long term performance
Resilience is a central reason many property owners consider steel roofing. Properly coated steel can withstand repeated cycles of rain, snow, wind, and sun exposure. The rigidity of the panels helps them resist impact from hail better than some materials, though very severe hail can still cause dents or surface damage that may need assessment.
In snowy regions, the smooth surface of steel roofing can help snow slide off more easily than rougher materials, reducing the weight that accumulates on the roof structure. Snow guards or similar devices are often used to control how snow sheds so that it does not fall suddenly in large amounts in front of doors or walkways.
Steel roofing is also resistant to problems such as rot, insect damage, and warping that can affect wood based products. However, its long term performance depends heavily on correct detailing. Edge treatments, flashing installation, fastener selection, and ventilation all affect how well the system manages moisture and thermal movement over time.
Installation process and key considerations
Installing steel roofing involves more than simply attaching panels to a deck. The process usually starts with evaluating the existing roof structure to confirm it can support the chosen system and meets local building codes. In some cases, old roofing is removed; in others, steel panels may be installed over an existing layer, provided code and manufacturer guidelines allow it.
Underlayment is typically applied to the roof deck to provide an additional moisture barrier. The steel panels or shingles are then laid out according to the manufacturer instructions, often starting at the eaves and working upward. Proper alignment is important, as misalignment can affect appearance and weather resistance. Flashing details around chimneys, skylights, valleys, and roof edges are critical to help prevent leaks.
Sound is another consideration. Many modern steel roofing systems, when installed over solid decking and underlayment, do not produce noticeably louder rain noise inside the home than traditional materials. Insulation and attic construction also influence perceived sound levels. Ventilation design is equally important, as it can influence both moisture control and energy performance.
Homeowners and building owners also need to consider local climate when selecting coatings and profiles. Coastal or highly industrial environments may expose roofs to more corrosive conditions, which can influence the choice of protective layers and fastener materials. Color selection may affect both aesthetics and thermal performance, since lighter colors generally reflect more solar energy.
Weighing benefits and considerations
Steel roofing offers a blend of durability, fire resistance, and design flexibility that has made it increasingly common on a wide range of buildings. Its long service life and potential energy benefits can align well with goals for reduced maintenance and more predictable performance over time.
At the same time, successful use of steel roofing depends on careful product selection, attention to installation details, and an understanding of local climate conditions. Considering factors such as profile type, coating system, roof structure, ventilation, and acoustic preferences helps ensure that the chosen system matches the needs of the building and its occupants.
By reviewing the main characteristics, types, and practical considerations of steel roofing, property owners and professionals can make more informed decisions about whether this material is an appropriate option for a given project and how to plan for its long term role in protecting the structure.