Emergency Generators for Home Power Backup Solutions
Power outages can strike unexpectedly, leaving households without electricity for hours or even days. Emergency generators provide a reliable solution for maintaining essential power during grid failures, ensuring comfort, safety, and functionality when traditional power sources fail. These backup power systems have become increasingly important as extreme weather events and aging electrical infrastructure make power interruptions more common across the United States.
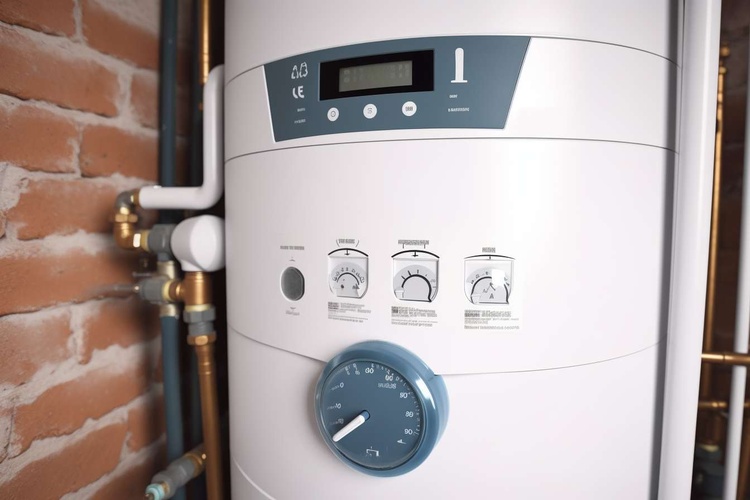

Home Power Generators: Essential Backup for Modern Living
In today’s connected world, reliable electricity is more than a convenience—it’s a necessity. Home power generators serve as critical backup systems that automatically or manually restore power during outages. These devices range from small portable units that can run a few essential appliances to whole-home systems capable of powering an entire residence seamlessly. The increasing frequency of severe weather events and aging electrical infrastructure in many areas has made generator ownership a practical consideration for millions of households. Beyond convenience, generators can protect food supplies, maintain heating or cooling systems, support home-based medical equipment, and keep security systems operational during extended outages.
Understanding Home Generator Types: Standby, Portable & Inverter
Home generators fall into three main categories, each with distinct advantages and applications. Standby generators are permanently installed outside the home and connected directly to the electrical system and fuel supply. These units automatically detect power loss and activate within seconds, providing seamless backup power without any manual intervention. They typically run on natural gas or propane and can power an entire home for extended periods.
Portable generators offer flexibility and lower upfront costs. These gasoline or dual-fuel units can be moved and stored when not in use, then deployed during outages. They require manual setup and connection to appliances through extension cords or a transfer switch. While they cannot power an entire home simultaneously, they provide sufficient capacity for essential circuits and appliances.
Inverter generators represent a newer technology that produces cleaner, more stable power suitable for sensitive electronics. These compact units operate more quietly than conventional portable generators and offer better fuel efficiency. They work well for powering computers, entertainment systems, and medical devices that require consistent voltage and frequency.
How to Select the Right Home Backup Generator for Your Needs
Choosing the appropriate generator requires careful assessment of your household’s power requirements and priorities. Start by identifying which appliances and systems you must keep running during an outage. Critical items typically include refrigerators, heating or cooling systems, lighting, well pumps, sump pumps, and medical equipment. Calculate the starting and running wattage for each device to determine your total power needs.
Consider the typical duration and frequency of outages in your area. If you experience brief, infrequent blackouts, a portable generator may suffice. For regions prone to extended outages from hurricanes, ice storms, or wildfires, a standby generator provides more comprehensive protection. Fuel availability also matters—natural gas standby units offer convenience if you have existing gas service, while portable generators require gasoline storage and periodic refueling.
Budget plays a significant role in generator selection. Portable generators generally cost between $400 and $3,000 depending on capacity and features. Standby generators represent a larger investment, with units typically ranging from $3,000 to $6,000 for the generator itself, plus installation costs. Inverter generators fall in the middle range, usually priced between $800 and $3,500. Operating costs, maintenance requirements, and fuel consumption should also factor into your decision.
| Generator Type | Power Range | Typical Cost Range | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Generator | 3,000-10,000 watts | $400-$3,000 | Manual operation, gasoline/propane fuel, movable, requires transfer switch or extension cords |
| Standby Generator | 7,000-20,000+ watts | $3,000-$6,000 (unit only) | Automatic activation, permanent installation, natural gas/propane, powers whole home |
| Inverter Generator | 1,000-7,000 watts | $800-$3,500 | Clean power for electronics, quiet operation, fuel efficient, compact design |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Professional Generator Installation: Ensuring Safety & Reliability
Proper installation is crucial for generator safety, performance, and longevity. Standby generators require professional installation by licensed electricians and often need permits and inspections. The installation process includes selecting an appropriate outdoor location with adequate ventilation, pouring a concrete pad or installing a mounting platform, connecting fuel lines, and integrating the generator with your home’s electrical system through a transfer switch.
Transfer switches are essential safety devices that prevent dangerous backfeeding—when generator power flows back into utility lines, potentially injuring utility workers or damaging equipment. Automatic transfer switches work with standby generators to seamlessly shift between utility and generator power. Manual transfer switches cost less but require homeowners to physically switch power sources during outages.
Even portable generators benefit from professional setup guidance. Proper grounding, correct cord sizing, and safe placement away from windows and vents prevent carbon monoxide poisoning and electrical hazards. Never operate generators indoors or in enclosed spaces, as exhaust contains deadly carbon monoxide that can accumulate rapidly. Position units at least 20 feet from your home with exhaust directed away from windows, doors, and air intakes.
Regular maintenance ensures your generator operates reliably when needed. Standby units should be serviced annually by qualified technicians who check oil levels, replace filters, test batteries, and verify proper operation. Portable generators require similar attention, including fuel stabilizer for long-term storage, periodic exercise runs, and spark plug replacement. Many manufacturers recommend running standby generators under load for 30 minutes monthly to keep components lubricated and identify potential issues before emergencies arise.
Investing in an emergency generator provides valuable protection for your home and family during power outages. By understanding the different types available, carefully assessing your needs, and ensuring proper installation and maintenance, you can select a backup power solution that delivers reliable performance when you need it most.