Vitamin C for Wrinkle Care and Skin Health 2026
Vitamin C is recognized for its role in skin health, particularly in supporting collagen production and protecting against oxidative damage. In the United States during 2026, both topical and dietary sources of Vitamin C continue to be studied for their effects on wrinkle reduction and skin appearance improvements.
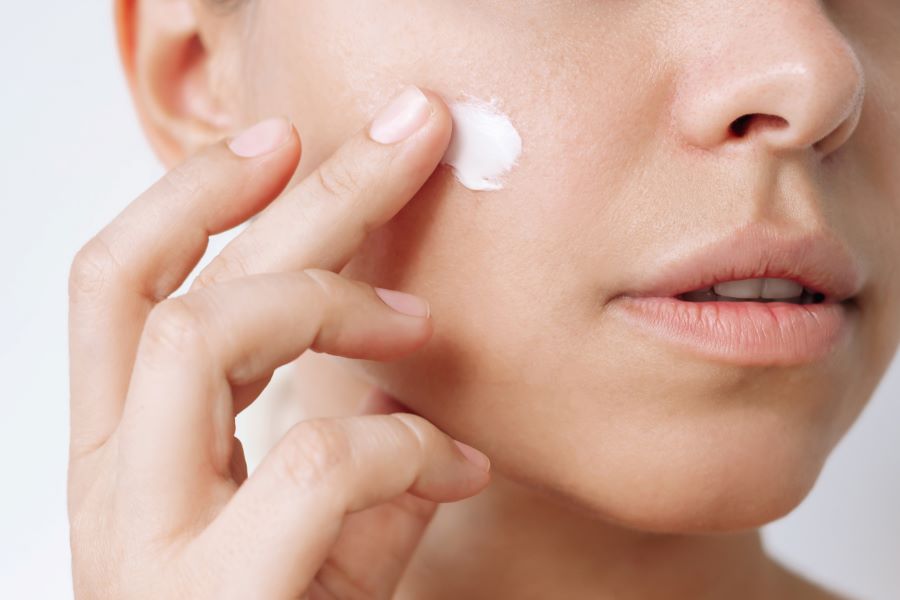

The Role of Vitamin C in Skin Health and Aging
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is an essential nutrient involved in various biological processes that affect skin health. It acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals generated by ultraviolet (UV) radiation and environmental pollutants. These free radicals contribute to the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, which can accelerate the formation of wrinkles and fine lines.
Collagen is a structural protein responsible for skin firmness and elasticity. Natural collagen production declines with age, starting as early as the late twenties to early thirties, which contributes to visible signs of aging including sagging skin and wrinkles. Vitamin C is necessary for the hydroxylation of proline and lysine, amino acids critical to collagen synthesis. Adequate Vitamin C levels support the maintenance and repair of collagen, thereby influencing skin texture and resilience.
Additionally, Vitamin C has been observed to have photoprotective properties by reducing UV-induced damage when applied topically. It may also aid in skin brightening by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which plays a role in melanin production.
Forms of Vitamin C Used in Skincare
In skincare formulations, Vitamin C is available in various derivatives, each differing in stability, absorption, and skin tolerability. Common forms include:
-
L-Ascorbic Acid: The pure form of Vitamin C, noted for its potency but limited stability. It is water-soluble and often formulated at concentrations of 10-20% for topical application.
-
Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP): A more stable, water-soluble derivative converted to ascorbic acid within the skin.
-
Ascorbyl Palmitate: Lipid-soluble, allowing better penetration of the skin’s lipid barrier with relatively higher stability.
-
Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate: A stable and water-soluble compound with reported antioxidant effects.
The choice of derivative affects product performance and user experience. L-ascorbic acid is generally considered the most effective in clinical studies but may cause irritation in sensitive skin. Derivatives may be preferred for their enhanced stability and tolerance.
Considerations for Selecting Vitamin C Products in the U.S.
When selecting Vitamin C products, factors such as skin type, formulation stability, concentration, and packaging should be considered:
-
Concentration: Topical efficacy is generally observed at concentrations between 10% and 20%. Lower concentrations may produce milder effects; higher concentrations risk irritation.
-
pH Level: Ascorbic acid requires a low pH (~3.5) for optimal skin penetration, which can influence tolerability.
-
Packaging: Vitamin C is sensitive to light and air, which can degrade the compound. Air-tight, opaque containers help maintain stability.
-
Skin Sensitivity: Individuals with sensitive or rosacea-prone skin may require formulations with derivatives or lower concentrations to reduce irritation risk.
Integration with Other Skincare Ingredients
Vitamin C is often incorporated in skincare routines alongside other actives that may complement or enhance its effects:
-
Vitamin E (Tocopherol): Acts synergistically with Vitamin C as an antioxidant barrier against lipid peroxidation.
-
Ferulic Acid: A plant-based antioxidant that stabilizes vitamins C and E, enhancing their photoprotective effects.
-
Retinoids: Known for their skin-renewing properties, combining Vitamin C with retinoids can support anti-aging efforts, though layering order and concentration should be managed to minimize irritation.
-
Peptides: These support collagen synthesis and can be combined with Vitamin C for potential additive benefits in skin firmness.
-
Sunscreens: Using Vitamin C with broad-spectrum sunscreens can improve protection against UV-induced oxidative stress.
Application Guidelines for Topical Vitamin C
-
Frequency: Vitamin C products are typically applied once or twice daily, often in the morning before sunscreen to capitalize on antioxidant protection against daily UV exposure.
-
Layering: After cleansing and toning, Vitamin C serums are applied before moisturizers and sunscreen.
-
Patch Testing: New users should perform patch tests to assess skin tolerance, particularly for formulations with higher concentrations of L-ascorbic acid.
-
Storage: To preserve potency, Vitamin C products should be stored in cool, dark environments and promptly used after opening.
Dietary Vitamin C and Skin Health
Oral intake of Vitamin C through diet or supplements supports overall skin health by contributing to systemic antioxidant defenses and collagen production processes. Common dietary sources include citrus fruits, tomatoes, green leafy vegetables, berries, and bell peppers, widely available in the U.S.
While topical application targets the skin directly, systemic Vitamin C availability is necessary for the biosynthesis and maintenance of skin structures. Individuals with insufficient dietary intake or increased physiological demand (e.g., older adults or smokers) may benefit from increased consumption, though high-dose supplementation should be discussed with healthcare providers.
Recent Trends and Research in 2026
Current research in 2026 continues to explore enhanced delivery systems for Vitamin C, including encapsulation in liposomes and nanoparticles to improve stability and skin penetration. Advances in cosmetic chemistry enable formulations combining Vitamin C with other potent actives while maintaining gentleness.
Dermatological advice in the United States emphasizes evidence-based, consistent application of Vitamin C as part of comprehensive skin care, which includes sun protection and managing environmental exposure. Researchers also focus on individual variability in response to Vitamin C, influenced by factors such as skin type, genetics, and existing skin conditions.
Typical Costs in United States (2026)
When considering Vitamin C skincare products in the U.S., typical price ranges include:
-
Basic option: Around $10 to $25 – includes straightforward serums or creams with lower concentrations or less stable formulations.
-
Standard option: Approximately $25 to $50 – generally offers better formulations with stabilized Vitamin C derivatives, optimal concentrations, and improved packaging.
-
Premium option: Typically $50 to $100+ – often includes advanced delivery technologies, combination with complementary ingredients (e.g., ferulic acid, peptides), and brand reputation.
Prices vary by retail channel, formulation type, and inclusion of additional active ingredients.
Summary
Vitamin C remains a well-studied nutrient for supporting skin health and potentially reducing wrinkles and signs of aging. Both topical and dietary sources contribute to its effects, with topical application targeting the skin directly and dietary intake supporting systemic needs. Selection of appropriate Vitamin C formulations and proper use aligned with individual skin needs can influence effectiveness. Ongoing research and product innovation in 2026 continue to refine understanding and use of Vitamin C in skincare within the United States.