Scalp Psoriasis Diagnosis and Treatment Options 2026
Scalp psoriasis is a common chronic skin condition affecting many individuals in the United States. It causes red, scaly patches on the scalp and may involve itching, irritation, and discomfort. Understanding its diagnosis and current treatment approaches is important for effective management in 2026.
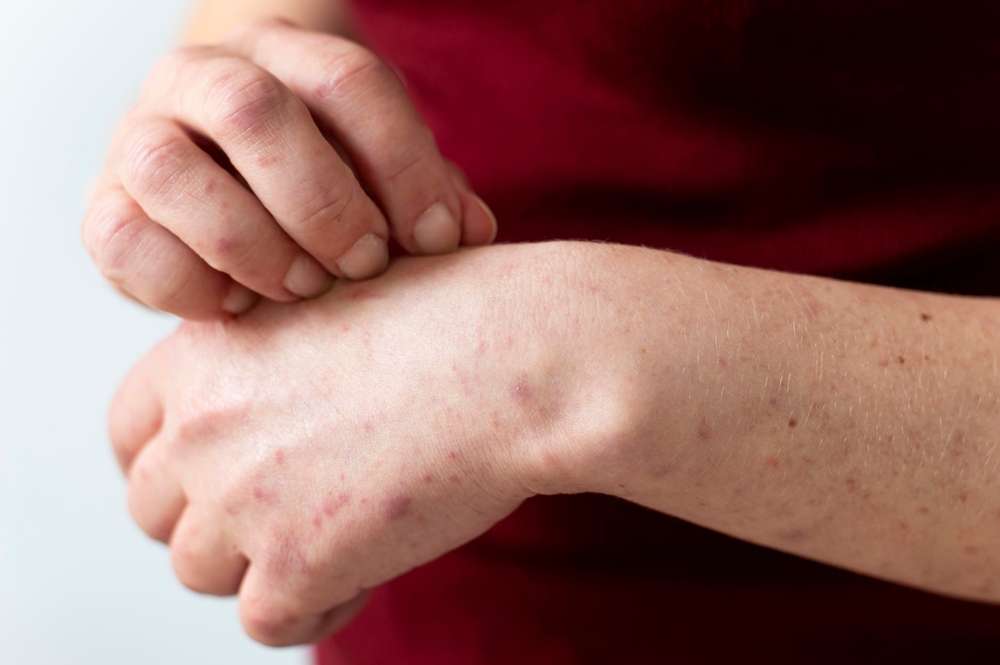
Understanding Scalp Psoriasis and Its Impact
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells that form thick, scaly patches. It is driven by an autoimmune response that causes inflammation and accelerated skin cell turnover. In the United States, approximately 45% to 56% of people living with psoriasis experience involvement of the scalp. The condition can extend beyond the scalp to areas such as the hairline, forehead, neck, and around the ears.
Symptoms of scalp psoriasis vary in severity, ranging from mild dandruff-like flaking to thick, silver-white plaque formations. Significant itching, burning sensations, and scaling are common. Severe cases may lead to temporary hair shedding due to inflammation. The visibility and chronic nature of scalp psoriasis can affect psychological well-being and quality of life for many individuals.
Diagnosis of Scalp Psoriasis
Accurate diagnosis of scalp psoriasis is essential because it shares symptoms with other scalp conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, and dandruff. In the United States, dermatologists primarily diagnose scalp psoriasis through clinical examination. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Detailed medical history review, including family history of psoriasis or autoimmune diseases
- Physical evaluation of the scalp and affected skin areas
- Assessment of scaling patterns, plaque thickness, and distribution
- Sometimes, skin biopsy may be performed when diagnosis is uncertain
In addition to skin symptoms, about one-third of psoriasis patients may develop psoriatic arthritis, an inflammatory joint condition. Early evaluation for joint symptoms is important to prevent progression and manage related health risks such as cardiovascular disease and mental health issues.
Common Symptoms and Triggers
Symptoms
Typical signs of scalp psoriasis include:
- Redness and inflammation of the scalp skin
- Thick, silvery-white scales or plaques
- Itching and burning sensations
- Dry scalp and flaking
- Possible hair thinning or temporary hair loss at inflamed areas
Triggers
Several factors can provoke or worsen scalp psoriasis flare-ups. These include:
- Stress and emotional strain
- Infections, including streptococcal throat infections
- Weather changes, especially cold and dry conditions
- Certain medications such as beta-blockers and lithium
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Mechanical irritation from scratching or harsh hair care products
Identifying and managing these triggers can help reduce flare frequency and severity.
Treatment Approaches in 2026
Treatment of scalp psoriasis focuses on reducing inflammation, slowing skin cell growth, and relieving symptoms. Treatment options vary according to severity and individual response.
Topical Treatments
Topical therapies are recommended as first-line treatment for mild to moderate scalp psoriasis. These include:
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and itching; available in various strengths and formulations such as shampoos, lotions, and foams.
- Vitamin D analogues (e.g., calcipotriene): Help normalize skin cell production.
- Coal tar preparations: Provide anti-inflammatory and anti-scaling effects.
- Salicylic acid: Helps remove scales to enhance penetration of other topical agents.
Applying topical treatments on the scalp can be challenging due to hair coverage. Patients are advised to follow usage instructions carefully to improve effectiveness.
Phototherapy
Light therapy using ultraviolet B (UVB) targeted at the scalp may be considered for moderate to severe cases or when topical treatments alone are insufficient. Phototherapy requires clinical supervision and specialized equipment.
Systemic Treatments
For extensive or resistant scalp psoriasis, systemic medications may be prescribed by healthcare providers. Available options include:
- Oral therapies: Such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or apremilast, which modulate immune response.
- Biologic agents: Target specific components of the immune system and are used primarily for moderate to severe psoriasis. Examples include tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and interleukin inhibitors.
These treatments require monitoring for potential side effects and interactions.
Emerging Therapies
Research continues to produce new treatments targeting immune pathways involved in psoriasis pathogenesis. In 2026, several novel agents with improved efficacy and safety profiles are being evaluated in clinical studies.
Living with Scalp Psoriasis
Managing scalp psoriasis often involves a multidisciplinary approach including dermatologists, primary care providers, and sometimes rheumatologists. Patients benefit from education about the chronic nature of the condition, trigger avoidance, and adherence to treatment plans.
Supportive care measures include:
- Using gentle hair care products without irritants
- Maintaining scalp hygiene
- Stress management techniques
- Regular medical follow-up for symptom monitoring
Typical Costs in United States (2026)
When considering diagnosis and treatment of scalp psoriasis in the United States, typical price ranges include:
- Basic option: Around $50 to $150 for initial dermatology consultation and topical medications suitable for mild cases.
- Standard option: Approximately $500 to $3,000 yearly, including prescription topical therapies, phototherapy sessions, and follow-up visits.
- Premium option: Typically $15,000 to $40,000 annually for biologic therapies or advanced systemic treatments, encompassing medication costs, clinical monitoring, and specialist care.
These costs can vary depending on insurance coverage, geographic location, and treatment complexity. Patients are advised to consult healthcare providers and insurers to understand individual coverage and expenses.