Affordable Compact Two-Seater Electric Cars in the United States for 2025 City Driving: Incentives and Benefits Explained
Small two-seater electric vehicles are an affordable, efficient option for many U.S. city commuters in 2025. This article explains why they suit urban use—covering costs, federal and state incentives, charging options, practical benefits, and environmental advantages.

Readers will discover how federal and state incentives help reduce the cost of ownership, what makes these vehicles ideally suited for city environments, and how charging infrastructure supports everyday urban mobility.
Understanding the Affordability of Small Two-Seater Electric Cars
Contrary to common perceptions of electric vehicles being prohibitively expensive, many small two-seater EVs in the United States come with price tags generally ranging from affordable economy vehicle levels. Before incentives, these vehicles typically fall between a lower and moderate price band that competes well with comparable gasoline cars aimed at city drivers. This pricing makes them accessible for individuals seeking compact and budget-conscious electric options.
Moreover, federal and state incentives dramatically enhance affordability:
-
Federal Tax Incentives: Under the Inflation Reduction Act, most buyers qualify for federal tax credits of up to $7,500, reducing the effective purchase price across the country.
-
State-Level Rebates: Many states supplement federal incentives with additional rebates or tax credits that may vary from roughly $1,000 to $5,000 or more. For example, certain state programs provide upfront rebates directly reducing the cost at dealerships.
Ultimately, combining these incentives with naturally low operating costs creates a financial advantage for urban commuters interested in sustainable transportation.
Lower Operating and Maintenance Costs for City Use
Owning a compact electric vehicle in an urban environment often results in substantial savings compared to gasoline-powered cars over time. These savings arise primarily from the following:
-
Fuel Cost Efficiency: Electric vehicles reduce fuel expenses significantly, with average annual savings of several hundred dollars due to higher energy efficiency and the lower cost of electricity compared to gasoline.
-
Reduced Maintenance Requirements: With electric motors that have fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes, maintenance tends to be simpler and less costly—limiting expenses by a few hundred dollars annually.
-
Insurance Considerations: Insurers often provide more favorable rates for smaller, lower-speed EVs designed for city use, further lowering total costs.
Urban drivers benefit uniquely from these savings, as frequent stop-and-go conditions favor EVs’ instant torque and energy recuperation technologies, enhancing efficiency.
Compact Design Optimized for Urban Environments
City driving demands vehicles that are easy to maneuver, park, and navigate through dense traffic. Small two-seater electric cars excel at these needs due to several design features:
-
Size and Dimensions: Many models measure under 10 feet in length, allowing them to fit into compact parking spaces unsuitable for larger cars.
-
Tight Turning Radius: Turning circles often range around 22 to 30 feet, making U-turns and lane changes simpler on narrow city streets.
-
Agile Performance: Instant electric torque provides smooth acceleration, ideal for traffic lights and crowded intersections.
These attributes result in a stress-reducing driving experience within metropolitan areas where space and convenience are at a premium.
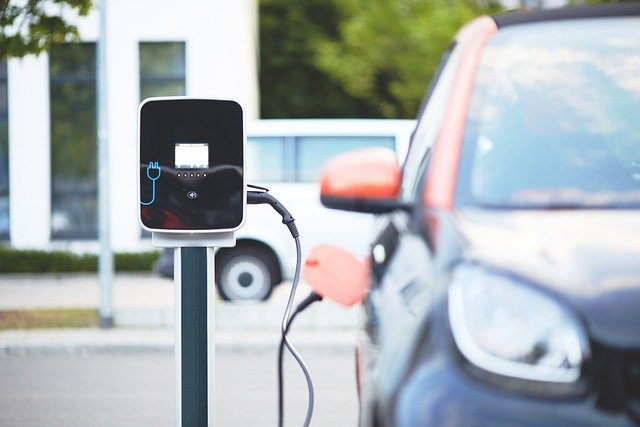
Battery Range and Charging Options for Daily Urban Commutes
Range anxiety is often a concern for new EV users. However, small two-seater electric cars typically offer driving ranges from approximately 80 to 150 miles per full charge. Considering that the average daily US commute is about 40 miles roundtrip, these vehicles provide sufficient range for most city driving needs.
Charging accessibility is supported by increasingly widespread infrastructure:
-
Home Charging: Standard 120V outlets (Level 1) allow overnight charging, adding a modest number of miles per hour. For faster home charging, 240V Level 2 chargers can replenish batteries in about 3 to 5 hours.
-
Public Fast Charging: A growing network of DC fast chargers enables quick top-ups within 30 to 60 minutes, supporting occasional longer trips.
As of 2025, over 50,000 public charging locations exist nationally, ensuring convenient access to energy supply for urban EV owners.
Government and Municipal Incentives Enhancing Urban EV Adoption
Beyond purchase incentives, many cities and states provide special benefits to electric vehicle owners that enhance their practicality in urban contexts:
-
Access to High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes regardless of passenger count, reducing commute times.
-
Free or discounted parking in designated EV spaces.
-
Rebates or credits for installing home charging stations.
For instance, certain state programs increase chargers’ accessibility in workplaces, multifamily housing, and public areas, often with increased support in disadvantaged communities to foster equitable transition.
Environmental Impact of Small Two-Seater Electric Vehicles
These compact EVs contribute positively to environmental sustainability:
-
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Compared to similar gasoline vehicles, lifetime emissions can be lowered by 50-70%, particularly in states with clean electricity grids.
-
Energy Efficiency: Lightweight design supports higher miles per kilowatt-hour energy use, improving overall electricity efficiency.
-
Battery Recycling: Advanced recycling programs recover a high percentage of critical materials from EV batteries, reducing resource consumption and waste.
Their smaller resource footprint and zero tailpipe emissions support ongoing climate goals in urban sectors.
Models and Trends Shaping the Compact EV Market
Several models exemplify key features making small two-seater electric cars well-suited to city life, such as ultra-compact size, efficient range, and maneuverability. Additionally, emerging affordable options from international manufacturers may soon increase market choices in the United States.
Potential buyers should research various models’ specifications and how they align with personal driving habits and charging access to optimize the ownership experience.
Conclusion
In 2025, small two-seater electric cars offer a compelling mix of affordability, urban practicality, and sustainability for city commuters in the United States. Supported by federal and state incentives, low running costs, and expanding charging infrastructure, these compact EVs provide an intelligent solution to the challenges of urban mobility. Interested consumers are encouraged to explore available options carefully to make informed decisions suited to their specific needs.
Disclaimer: Prices, incentives, rebates, and availability mentioned in this article vary by region, dealer, and over time. Consumers should verify current offers and conditions with local authorities, dealerships, or official state programs. Incentive programs and terms are subject to change.
Sources
-
New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA): 2025 EV Incentives and Programs
-
Electrek: 2025 Electric Vehicle Tax Credits and Rebates in the United States
-
BrowseBrain: Overview and Insights on Small Two-Seater Electric Cars in the US Market